What Defines a Brand Positioning Strategy?
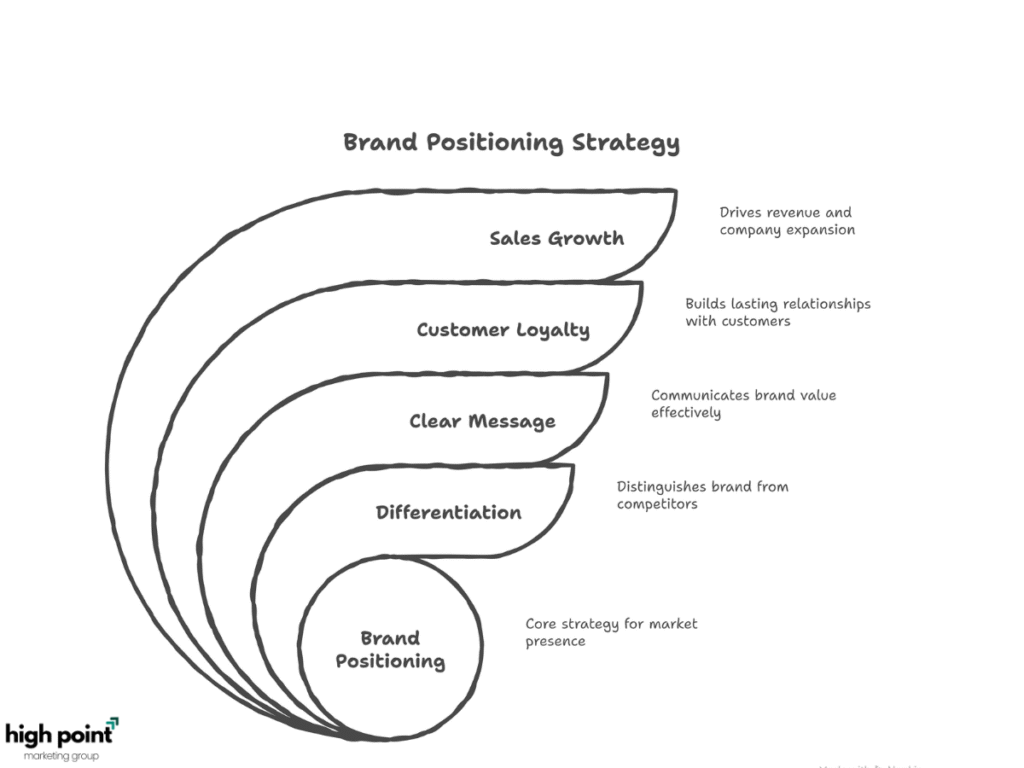
A brand positioning strategy is a company’s plan to create a special and unique image for its brand in the minds of customers.
The primary goal is to differentiate the brand from competitors by highlighting its unique qualities. This helps customers understand the brand’s unique value and gives them a clear reason to choose it.
How is a brand positioning strategy developed?
To develop a brand positioning strategy, companies follow a clear plan:
- Look Inward and Outward: First, they study their brand and what their competitors are doing.
- Know the Customer: Next, they figure out exactly who their target customers are.
- Find What’s Special: Then, they decide what makes their brand unique and different from all the others.
- Create and Share the Message: Finally, they create a clear message about why their brand is special and share it everywhere.
What are the components of a brand positioning strategy?
A brand positioning strategy is made up of a few key parts:
- Your Customer & Competitors: Knowing who you sell to and who you are competing against.
- Your Special Offer: Figuring out what makes your brand unique and the promise you make to customers.
- Your Look & Feel: Deciding on your brand’s personality, logo, colors, and how it “talks” to people.
- Your Purpose: Being clear about what your brand stands for and its main goals.
Why is a brand positioning strategy important?
A brand positioning strategy is crucial because it enables a business to differentiate itself from its competitors. It creates a clear message that tells customers why your brand is special and the best choice for them. This builds strong customer loyalty, which leads to more sales and helps the company grow. It also keeps all marketing efforts focused and consistent.
What Are the Types of Brand Positioning Strategies?
Here are some common types of brand positioning, explained simply:
- Price or Quality: Focusing on being the cheapest option or the very best quality available.
- Convenience or Service: Highlighting that the brand is the easiest to use or has the most helpful customer support.
- Problem or Benefit: Showing how the brand solves a specific problem or offers a unique benefit no one else does.
- Competitors: Defining the brand by showing how it is different from or better than the competition.
- Lifestyle or Feeling: Connecting the brand to a certain lifestyle, emotion, or a set of values.
How does a price-based positioning strategy work?
A price-based positioning strategy works by using a product’s price to send a clear message to customers.
A low price is used to position the brand as the most affordable option, attracting many buyers. A high price creates a perception of premium quality and exclusivity. Setting a similar price to competitors positions the brand as a direct alternative.
How does a quality-based positioning strategy work?
Quality-based positioning strategy is a way to show that a brand is quite special and of a very high standard.
It works by gently pointing to the brand’s excellent materials, great performance, or long-lasting durability. This approach is often for customers who value this high quality and are willing to pay a bit more. The higher price itself helps to signal that the brand is a premium and trustworthy choice.
How does a convenience-based positioning strategy work?
Convenience-based positioning strategy works by focusing on one simple goal: making life easier for the customer.
It highlights how a product or service is faster, simpler to use, or easier to get than any of the competitors. This strategy is perfect for attracting busy customers who are often willing to pay a little more to save time and avoid hassle.

How does a differentiation strategy work?
A differentiation strategy works by making your business unique and superior compared to competitors. The goal is to identify what makes you special and communicate that value to customers.
Here is how it works in short:
1. Offer a Unique Value
Provide something competitors don’t, like unique features, better quality, or a special customer experience that people truly value.
2. Communicate Your Uniqueness
Clearly show customers why you are different and better in your marketing and messaging to build a strong reputation.
3. Win in the Market
This unique value allows you to either charge a higher price or win more customers at the same price as competitors.
How does an emotional positioning strategy work?
An emotional positioning strategy works by connecting with a customer’s feelings, values, and dreams, not just their practical needs.
It focuses on how the brand makes someone feel, such as confident, happy, or safe. The goal is to build a deep, personal connection that creates strong loyalty and trust, turning customers into loyal fans who feel like they are part of a community.
What Are Examples of a Brand Positioning Strategy?
Here are a few short examples of famous brand positioning strategies:
- Walmart: Focuses on low prices with its “Everyday Low Prices” strategy.
- Apple: Positions itself as a premium and high-quality innovator.
- Amazon: Focuses on convenience with fast, easy delivery.
- Nike: Uses emotion, positioning itself around empowerment with “Just Do It.”
- Tesla: Combines sustainability with high performance to stand out.
- Coca-Cola: Positions itself around the feeling of happiness and connection.
What is a positioning strategy example in the technology industry?
Here are a few short examples of positioning strategies in the tech industry:
- Tesla: Focuses on combining sustainability with high performance.
- Samsung: Positions its phones around having the newest features and technology.
- Dyson: Highlights its unique and innovative technology in home appliances.
- Microsoft: Adapted its strategy by shifting focus to cloud-based services.
What is a positioning strategy example in the retail industry?
Let’s look at a few simple examples of positioning strategies in retail:
- Aldi: Positions itself as a budget-friendly grocery option with low prices.
- Lidl: Differentiates by selling unique private label products (like its own brand of cola) instead of major national brands.
- Apple Stores: Positioned as a premium and high-quality shopping destination for technology.
- Convenience: A grocery store selling pre-cut vegetables positions itself on convenience to save customers time.
What is a positioning strategy example in the automotive industry?
Here are a few short examples of positioning strategies in the car industry:
- Volvo: Positions itself as the safest car brand.
- Toyota: Focuses on being reliable and durable.
- Tesla: Positions itself around innovation and sustainability.
- BMW: Focuses on performance and the driving experience.
- Mercedes-Benz: Positions itself as a symbol of luxury and quality.
- Lexus: Offers luxury quality at a better value.
How Is a Brand Position Statement Created?
Creating a brand positioning statement is a simple process. First, you research your target customers and competitors to understand your market. Then, you define what makes your brand different and the unique value you offer. Finally, you combine these insights into a short, internal statement explaining who you help, what you offer, and why you’re the best choice.
What is the purpose of a brand position statement?
The main purpose of a brand positioning statement is to act as an internal guide for your company. It is a short, clear statement that defines who your target customer is, what makes your brand unique, and how you are different from competitors. This keeps your entire team aligned and focused, ensuring all marketing and business decisions tell the same consistent story.
What are examples of a brand position statement?
Brand positioning statements are short internal guides that define a brand’s unique value. For example, Volvo’s statement targets “upscale American families” with the promise of “maximum safety,” while Voss targets “upscale consumers” with a “luxurious drinking experience.” Similarly, Nike focuses on athletes seeking performance, while Apple targets tech-savvy consumers who want innovation. These examples typically follow a simple formula: For [target customer], [brand] is the [category] that offers [unique benefit].
How Does Marketing Leverage a Brand Positioning Strategy?
Marketing leverages a brand positioning strategy, High Point Marketing Group, as a roadmap for all its activities. The strategy informs marketing on what message to convey to customers and how to differentiate itself from competitors. It guides every decision, from advertising and pricing to social media and events, to ensure the brand’s story is consistent and memorable. This helps attract the right audience, build loyalty, and ultimately, drive sales. Market expansion for Non-Profit Organizations
How does branding relate to a positioning strategy?
The relationship is simple: positioning is the strategy, and branding is the execution.
First, your positioning strategy decides what you want your brand to be known for, like being the safest, cheapest, or most innovative option. Then, your branding brings that strategy to life through all the things customers see and feel, such as your logo, colors, and the tone of your messaging.

What are the characteristics of successful brand positioning?
The characteristics of successful brand positioning are foundational marketing principles used by brands like Apple, Tesla, and Coca-Cola, which include clarity, consistency, and competitiveness. These characteristics serve to create a unique identity in the consumer’s mind, providing a competitive advantage and guiding marketing efforts. Studies show consistent branding can boost revenue by over 30%, supporting Al Ries’ and Jack Trout’s definition that “Positioning is what you do to the mind of the prospect.” The key benefit is building brand equity, which enables premium pricing and customer loyalty. This concept is complemented by brand identity, which includes the tangible logos and designs that express the strategic position. Brand Managers and Marketers use these principles to develop a cohesive marketing strategy. The origin of this concept is credited to Al Ries and Jack Trout in their Advertising Age articles starting in 1969. The core sub-parts of successful positioning include clarity, consistency, credibility, competitiveness, and relevance.
Should you consider the disadvantages of a brand positioning strategy?
Yes, it is very important to consider the disadvantages. A poorly chosen strategy can confuse customers or cause the brand to fail. Specific plans have unique risks; for example, focusing only on a low price can make customers think your product is low-quality. Changing your position can also upset your most loyal customers. Since a bad strategy can waste resources and is very hard to fix, it’s crucial to think about the potential problems from the start.


