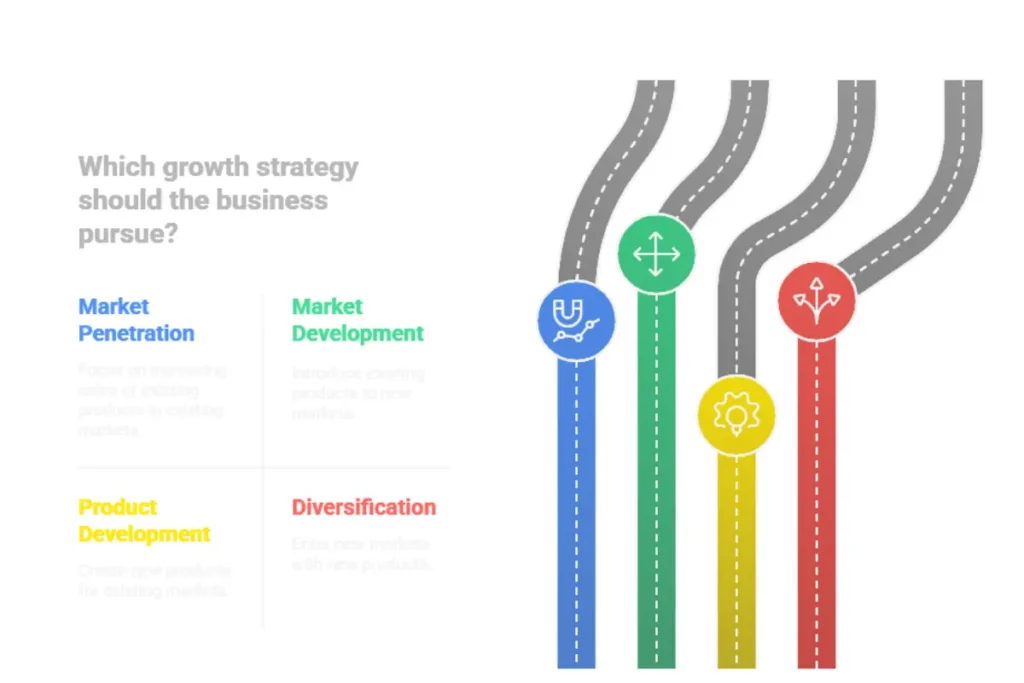
What Is the Ansoff Matrix?
The Ansoff Matrix, also known as the Product/Market Expansion Grid, is a strategic framework developed by Igor Ansoff in 1957. It helps businesses assess and plan growth strategies by evaluating different options for product and market expansion. This two-by-two matrix considers four key growth strategies, each varying in risk:
What are its four growth strategies?
The Ansoff Matrix identifies four key growth strategies that businesses can use to expand their market presence. Each strategy involves different levels of risk and focuses on either existing or new products and markets.
The Four Growth Strategies:
- Market Penetration
- Focuses on increasing sales of existing products within current markets.
- Common strategies include increasing marketing efforts, lowering prices, acquiring competitors, or enhancing distribution.
- Market Development
- Involves expanding existing products into new markets.
- This can include targeting new customer segments, entering new geographical regions, or exploring international markets.
- Product Development
- Focuses on creating new products for existing markets.
- Companies leverage customer loyalty or evolving needs to introduce innovative offerings or enhance existing products.
- Diversification
- The riskiest strategy is involving new products in new markets.
- It can be related diversification (introducing products that complement existing offerings) or unrelated diversification (entering entirely new industries).
Each strategy varies in its level of risk, with market penetration being the least risky and diversification the most risky. The Ansoff Matrix helps businesses assess these options and choose the best path for growth.
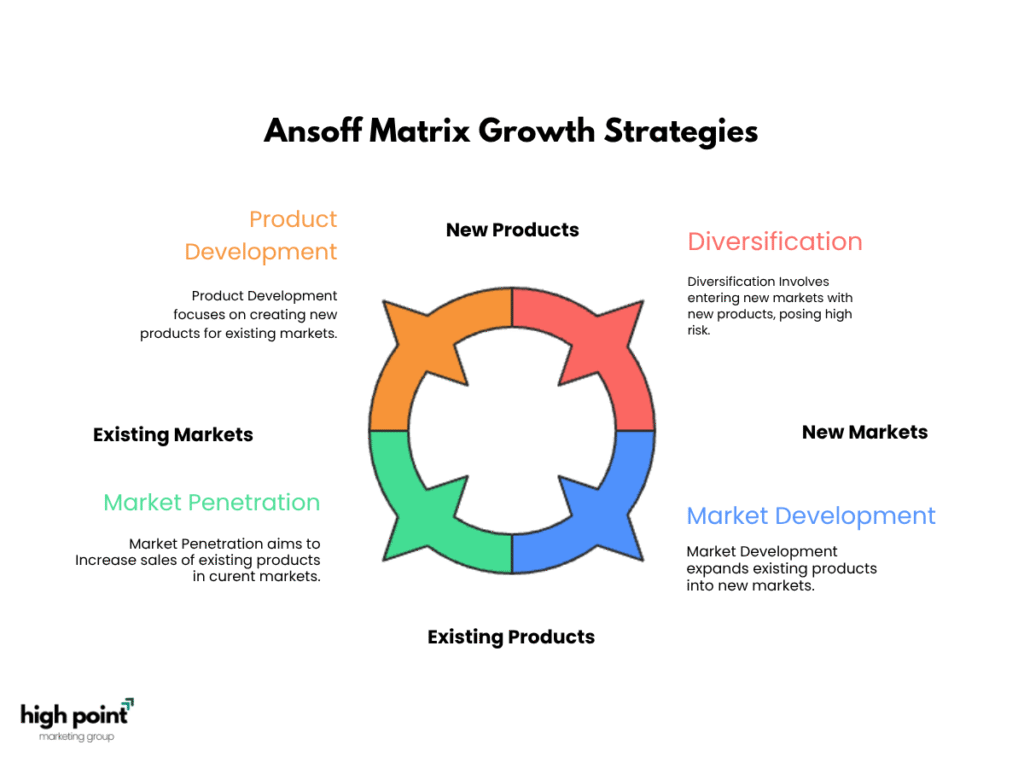
How Does the Ansoff Matrix Analyze Growth Opportunities?
The Ansoff Matrix analyzes growth opportunities by evaluating strategies based on existing or new products and markets. It helps businesses assess risk and determine the best growth path, whether through market penetration, product development, market development, or diversification, each varying in complexity and potential reward.
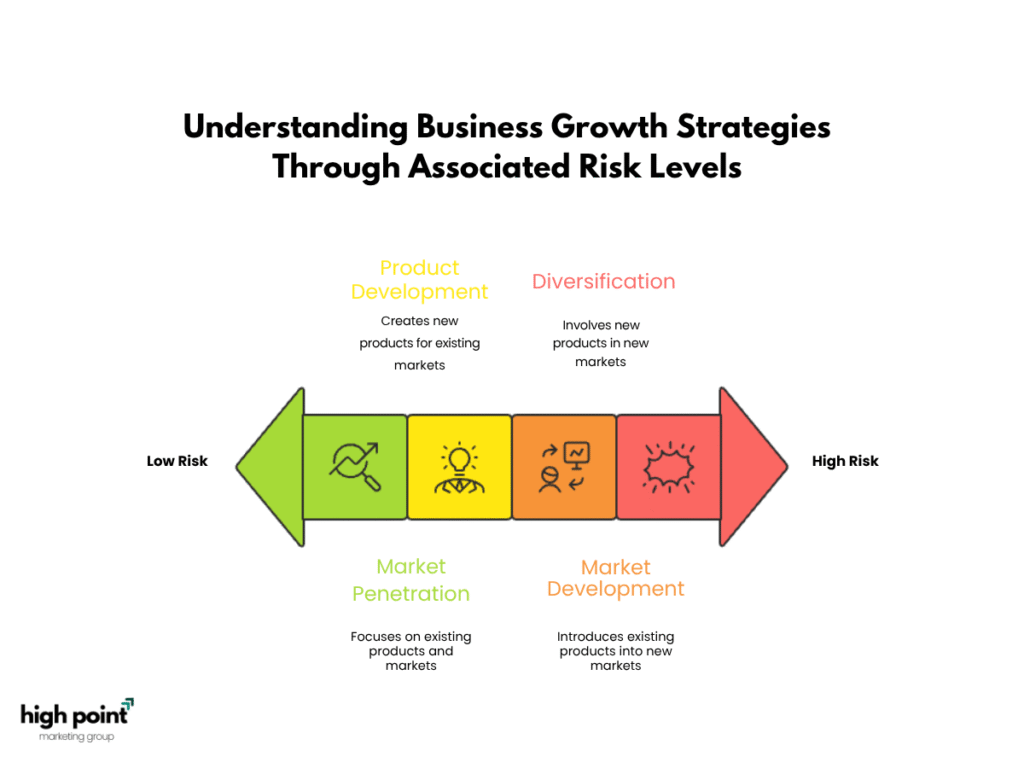
How does the Ansoff Matrix assess strategic risk?
The Ansoff Matrix assesses strategic risk by categorizing four growth strategies- Market Penetration, Market Development, Product Development, and Diversification—based on their varying levels of risk. These strategies are visually organized in a 2×2 grid, allowing businesses to weigh the associated risks and rewards before making decisions.
Risk Levels:
- Market Penetration: Involves the lowest risk, focusing on existing products and markets.
- Market Development: Increases risk by introducing existing products into new markets.
- Product Development: Carries moderate risk, as it involves creating new products for existing markets.
- Diversification: The highest risk strategy, involving new products in new markets.
By providing a structured framework, the Ansoff Matrix allows companies to evaluate the relative risks of each strategy. As businesses move away from their familiar products and markets, the risk increases. This helps businesses make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively, ensuring that growth strategies align with their risk tolerance and objectives.
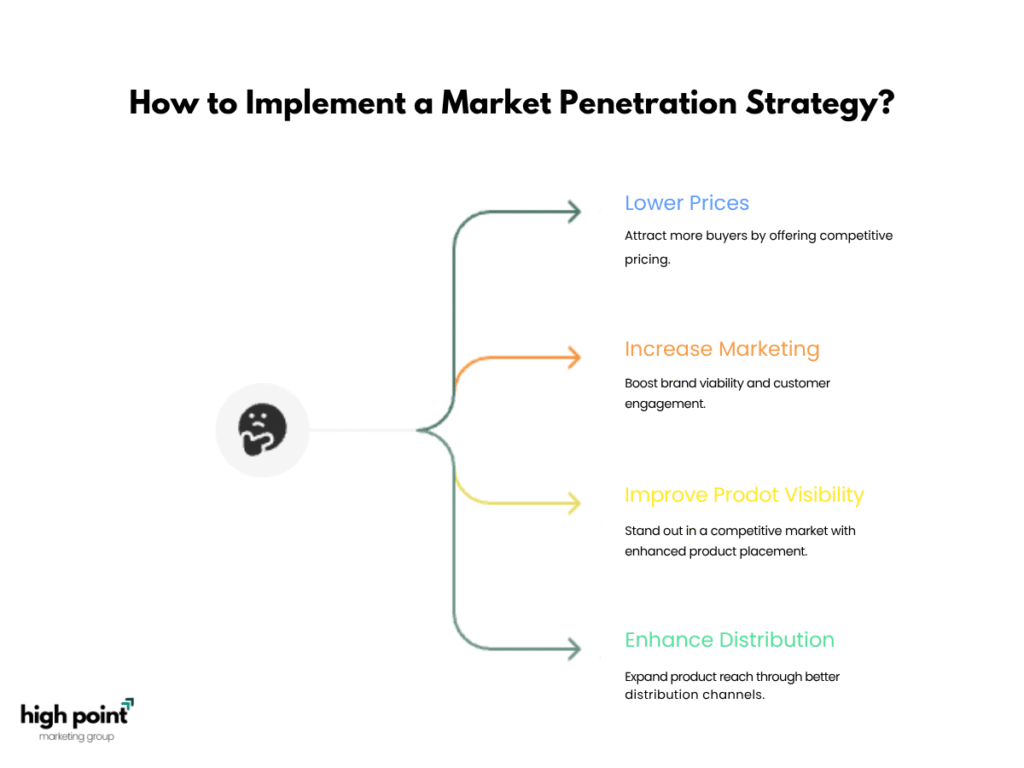
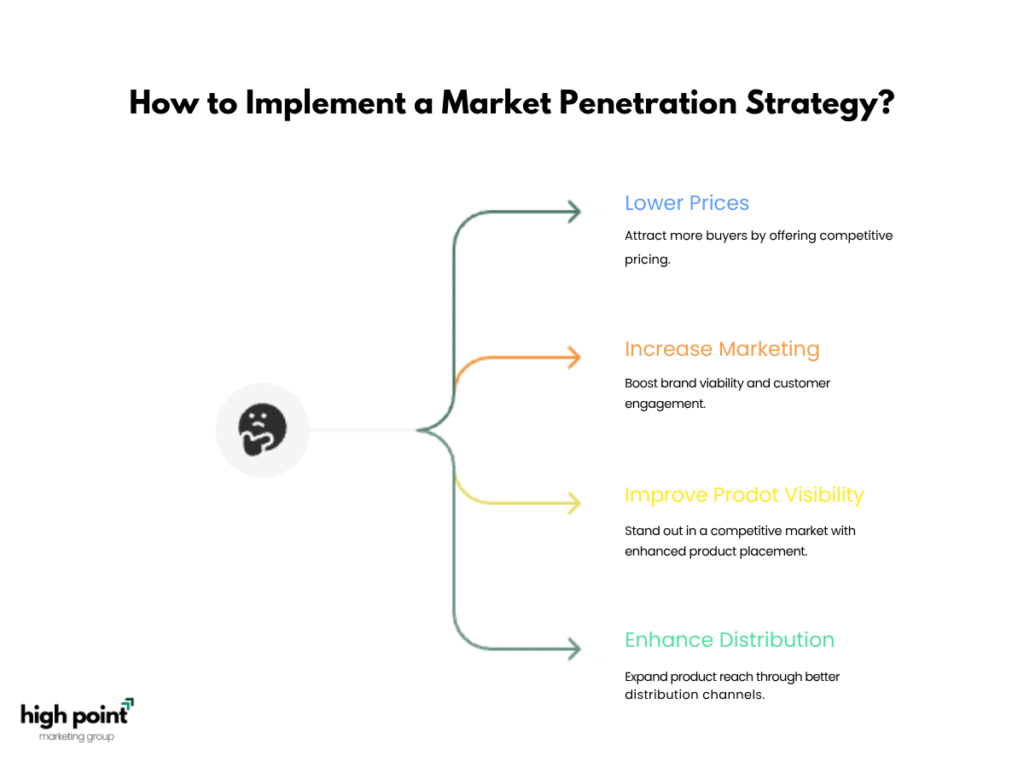
What is the Market Penetration strategy?
The Market Penetration strategy is a business growth approach where companies aim to increase their market share by selling existing products or services within existing markets. The main goal is to expand the customer base or encourage more frequent purchases from current customers.
Key Tactics:
- Lowering prices to attract more buyers.
- Increasing marketing efforts to boost brand visibility.
- Improving product visibility to stand out in a competitive market.
- Enhancing distribution channels for better product reach.
This strategy is considered low risk as it involves familiar products and markets. It is a widely used approach for growing a business by increasing sales through competitive pricing, aggressive marketing, and customer retention efforts.
What is the Product Development strategy?
The Product Development strategy is a business approach aimed at creating new products or improving existing ones to meet customer needs and foster growth. This strategy involves market research, product testing, and innovation to develop products that either enhance current offerings or introduce entirely new ones.
Key Elements:
- Goal: Expand or improve the product lineup to capture new market opportunities or boost competitiveness.
- Methods: Includes continuous feedback, iterative development, and testing to ensure alignment with market demand.
- Process: Combines research, design, and cross-functional collaboration to refine and launch successful products that meet customer expectations and business objectives.
This strategy is essential for businesses looking to stay competitive and responsive to changing market needs.
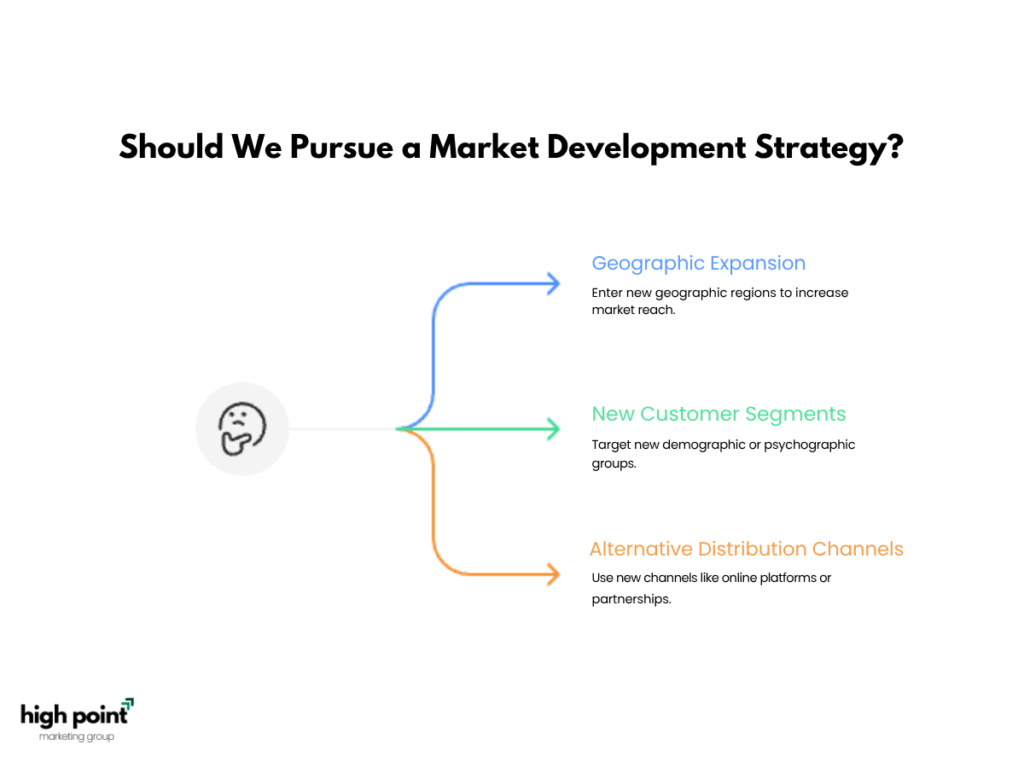
What is the Market Development strategy?
The Market Development strategy is a growth approach where businesses introduce existing products or services to new markets or customer segments.
Key Elements:
- Definition: It involves identifying and targeting new market segments for current products.
- Goal: The strategy seeks to expand the product’s reach and increase sales by entering new markets, whether geographic or demographic.
- Methods: Common methods include geographic expansion, targeting new customer segments, or utilizing alternative distribution channels.
- Risk: Market development is considered a low-risk strategy because it leverages existing products without requiring significant changes.
This strategy helps businesses boost market presence and sales by reaching new, untapped markets with their current offerings.
What is the Diversification strategy?
Diversification is a corporate strategy used by businesses to drive growth by expanding into new products, services, or markets. It helps reduce risks and capture new opportunities, allowing companies to move beyond their current operations and enter unrelated industries or product lines.
Key Points:
- Growth Strategy: Expanding operations through new products, services, or markets.
- Types of Diversification:
- Horizontal: New products within the same industry.
- Vertical: Control over supply chains or production.
- Conglomerate: Entering unrelated markets or industries.
- Risk Reduction: Reduces reliance on existing products or markets.
- Market Expansion: Entry into new geographical or industry markets.
- Goal: To fuel growth and secure the business against volatility.
Reasons for Diversification:
- Mitigates risks and offers a competitive edge.
- Driven by innovation, market shifts, or the need for higher revenue potential.
How Is the Ansoff Matrix Applied With Examples?
The Ansoff Matrix is a strategic tool that helps businesses plan growth by analyzing products and markets. It outlines four strategies:
- Market Penetration: Increase market share in existing markets with current products.
- Example: Boosting marketing efforts to attract more customers.
- Example: Boosting marketing efforts to attract more customers.
- Product Development: Introduce new products to existing markets.
- Example: A tech company adds new features to its software.
- Example: A tech company adds new features to its software.
- Market Development: Enter new markets with existing products.
- Example: Expanding into international markets.
- Example: Expanding into international markets.
- Diversification: Create new products for new markets.
- Example: A retailer offering financial products like credit cards.
The matrix helps businesses assess risks and opportunities, guiding growth strategies for market expansion or product innovation.
Which companies use a Market Penetration strategy?
Market penetration is a strategy to increase market share by promoting existing products in current markets. Companies use tactics like pricing adjustments, expanding distribution, and improving products.
Examples of Companies Using Market Penetration:
- Netflix: Offers free trials to attract customers.
- Amazon: Uses aggressive pricing and broad distribution.
- Coca-Cola: Innovates products to maintain market dominance.
- Apple: Grows through brand loyalty and product updates.
- McDonald’s: Uses pricing and promotions to expand globally.
- Starbucks: Opens stores in high-traffic areas.
- Lenskart: Offers affordable eyewear and expands market reach.
These companies strengthen their position through improved products, strategic pricing, and marketing efforts. Wants to know more about go here Strategic Planning & Consulting Plans
Which companies use a Product Development strategy?
Product Development is a strategy used by companies to introduce new products or improve existing ones.
Examples:
- Google: Focuses on continuous innovation.
- Amazon: Regularly updates services, especially in cloud computing.
- Netflix: Invests in original content.
- Zoom: Innovates its video conferencing features.
- Revolut: Expands its financial services.
- Apple: Regularly updates its product line.
- HubSpot: Innovates in marketing and CRM solutions.
These companies use product development to stay competitive and meet customer needs.
Which companies use a Market Development strategy?
Market Development is a growth strategy where companies introduce existing products to new markets or customer segments.
Companies Using Market Development Strategies:
- McDonald’s: Expanded globally, bringing its fast-food offerings to international markets.
- Starbucks: Entered new geographical markets, adapting products to local preferences.
- Coca-Cola: Launched new variants like Coke Zero to target different customer segments.
- Walmart: Expanded into new geographic markets, both domestically and internationally.
These companies—McDonald’s, Starbucks, Coca-Cola, and Walmart—use Market Development strategies to broaden their reach, targeting new markets and customer segments to drive growth.
Which companies use a Diversification strategy?
Diversification is a strategy where companies expand into new markets or product lines to reduce risk and foster growth.
Examples:
- Apple: Entered the financial services market.
- Netflix: Evolved from DVD rentals to streaming.
- General Electric: Diversified across industries.
- Walt Disney: Expanded into theme parks and entertainment.
- Amazon: Moved from e-commerce to cloud computing.
- 3M: Entered various industries like medical equipment.
These companies use diversification to reduce reliance on a single product or market and explore new revenue opportunities.
Should You Use the Ansoff Matrix for Strategic Planning?
The Ansoff Matrix is a strategic tool that helps businesses evaluate growth opportunities by analyzing existing and new products in current and new markets. It categorizes growth strategies into four types: market penetration, product development, market development, and diversification.
Benefits:
- Purpose: Helps businesses decide on the best growth strategy.
- Risk Assessment: Assesses the risks of each strategy.
- Strategic Alignment: Aligns business goals with growth strategies.
The Ansoff Matrix is an effective tool for making informed decisions, identifying new opportunities, and planning for long-term growth.
What are the advantages of applying the Ansoff Matrix?
The Ansoff Matrix is a strategic tool that helps businesses evaluate growth opportunities by analyzing existing products and new markets.
Key Advantages:
- Clarity: Divides strategies into four areas—market penetration, product development, market development, and diversification, making it easy to identify opportunities.
- Risk Assessment: Helps businesses evaluate risks associated with each strategy.
- Strategic Alignment: Aligns business goals with the best growth strategy for long-term success.
The Ansoff Matrix aids in strategic planning by providing a clear, structured approach to making informed growth decisions.

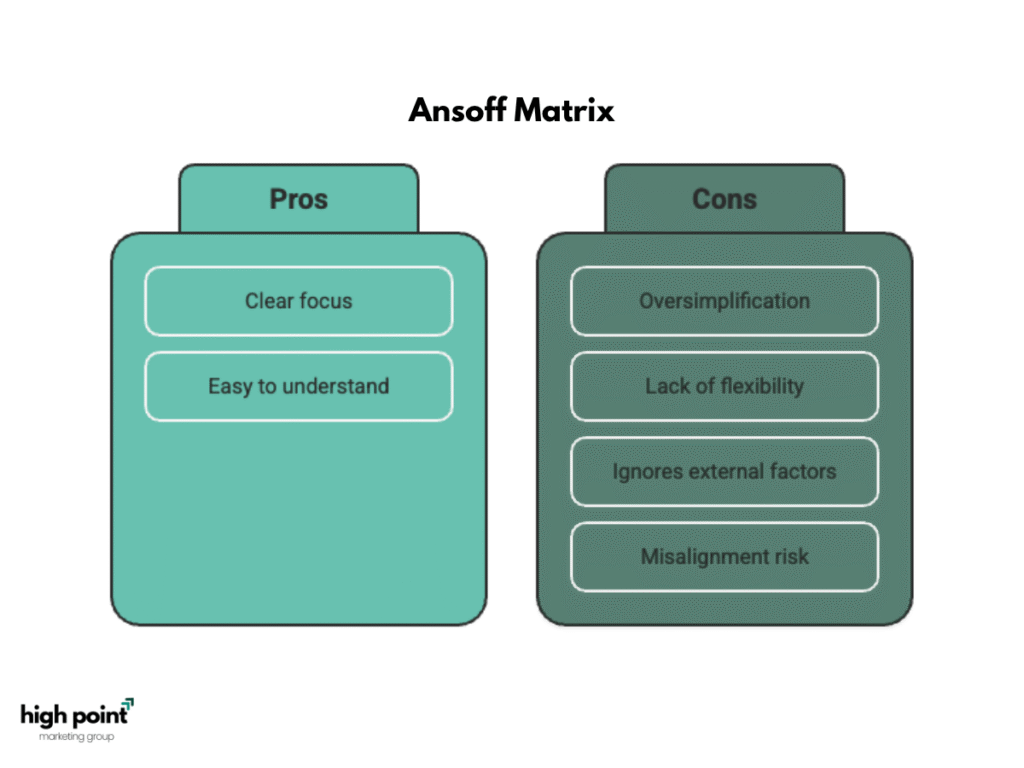
What are the disadvantages of applying the Ansoff Matrix?
The Ansoff Matrix simplifies strategic decisions, focusing only on product and market growth, which can lead to missed opportunities or conflicting objectives.
Key Disadvantages:
- Oversimplification: Can overlook complex business challenges.
- Lack of Flexibility: Not adaptable to rapidly changing environments.
- Exclusion of External Factors: Ignores competition and market conditions.
- Risk of Misalignment: Strategies may not align with broader company goals.
The matrix doesn’t fully address real-world complexities, limiting its usefulness in dynamic markets.
How Do Other Frameworks Compare to the Ansoff Matrix?
The Ansoff Matrix focuses on product and market growth strategies. However, other frameworks serve different purposes:
- Ansoff Matrix: Ideal for businesses looking to expand products and markets.
- Porter’s Generic Strategies: Helps companies position themselves competitively through cost leadership, differentiation, or focus.
- Blue Ocean Strategy: Aims to create new market spaces, avoiding direct competition.
While the Ansoff Matrix focuses on growth, other frameworks like Porter’s and Blue Ocean Strategy offer insights into competitive positioning or entering untapped markets.
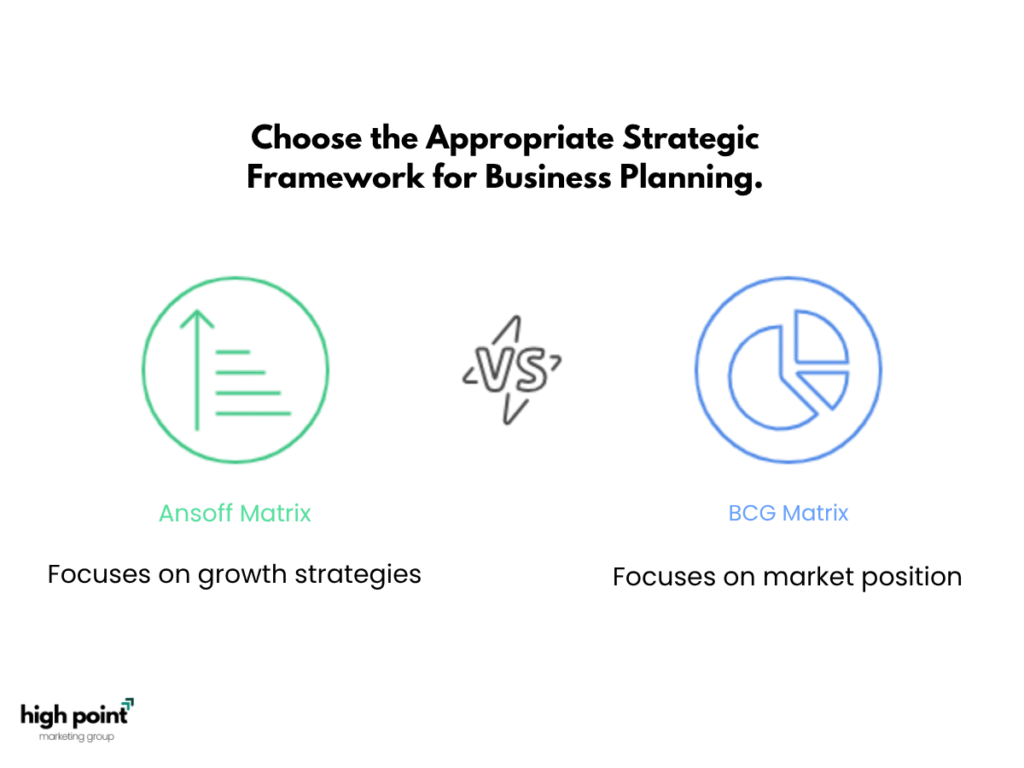
What is the difference between the BCG Matrix and the Ansoff Matrix?
The BCG Matrix focuses on managing existing product portfolios by analyzing market share and growth rate, categorizing products into Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs.
The Ansoff Matrix, on the other hand, is used for growth strategies, considering both product and market factors. It offers four strategies: Market Penetration, Product Development, Market Development, and Diversification. Ansoff Matrix On Wikipedia
In short, the BCG Matrix evaluates the current market position of products, while the Ansoff Matrix helps businesses plan future growth by expanding products and markets.
What are the primary alternatives to the Ansoff Matrix?
Primary Alternatives to the Ansoff Matrix:
- BCG Matrix: Focuses on managing product portfolios by market share and growth, categorizing products as Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs.
- PEST Analysis: Examines external factors (Political, Economic, Social, Technological) to understand market dynamics.
- McKinsey 7S Model: Aligns internal elements (Strategy, Structure, Systems, etc.) to ensure effective strategy execution.
- Porter’s Five Forces: Analyzes competitive forces (e.g., rivalry, threat of new entrants) to assess market attractiveness.
- 9-Box Grid: Offers a granular view of growth opportunities, expanding beyond the Ansoff Matrix’s options.
These frameworks complement the Ansoff Matrix, providing different insights into strategic planning, from market conditions to internal alignment.